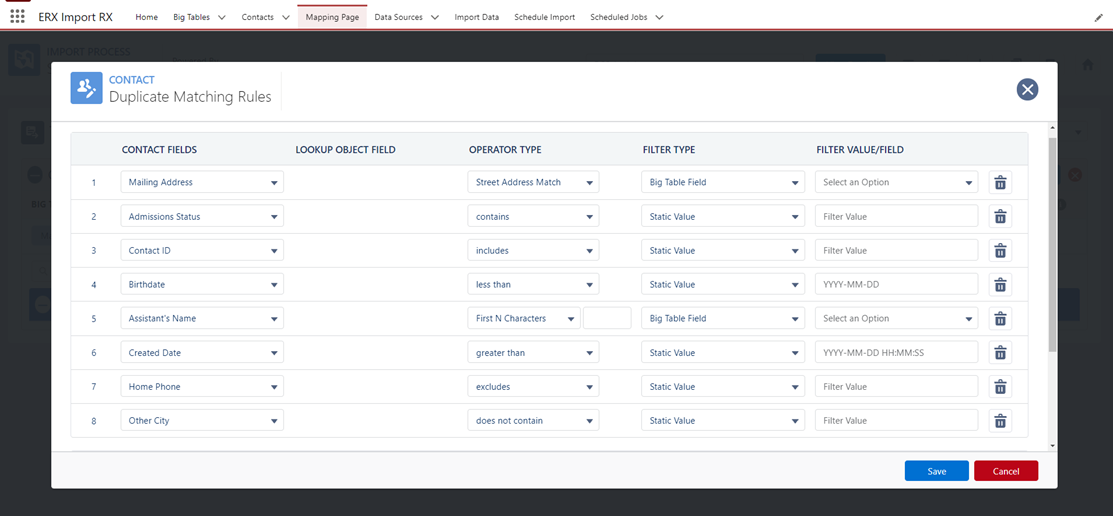
Duplicate Matching Rules Operators
Below are explanations of how the different operators work for the purposes of duplicate matching. The operators compare the value from the target object field, which we will call “Target,” with a value from the Big Table record or a static value, which we will call “Source.” All operators are case insensitive, e.g. “TEST” and “test” are treated the same.
| Operator | Rule |
|---|---|
|
Equals |
Target must equal Source |
|
Not Equals |
Target must not equal Source |
|
Starts With |
Target must begin with the value in Source, with any or no other characters at the end of Target |
|
Contains |
The characters in the Source value must be within the Target value, with any or no other characters at the beginning and end of Target |
|
Does Not Contain |
The characters in the Source value cannot be found within the Target value |
|
Less Than |
The value in Target must be less than the value in Source |
|
Greater Than |
The value in Target must be greater than the value in Source |
|
Less or Equal |
The value in Target must be less than or equal to the value in Source |
|
Greater or Equal |
The value in Target must be greater than or equal to the value in Source |
|
Includes |
Target is equal to a value listed in Source. Multiple values may be separate with commas. Do not put spaces after the commas |
|
Excludes |
Target is not equal to any value listed in Source. Multiple values may be separated with commas. Do not put spaces after the commas |
|
Street Address Match |
Special type of matching useful for street addresses that compares certain values in Target and Source while ignoring others. For example, the street number will be compared but common designators like “Avenue” or “Apt” will be ignore |
|
NA Phone Match |
Special type of matching only available if the Target field is of type “phone.” All non-numeric characters will be ignore and then a partial match is done |
|
First N Characters |
The first specified number of characters in Target must equal the same characters in Source |
|
First Name Match |
The value in Target must match Source or a corresponding nickname from a table of names. The table is found under Setup | Custom Metadata Types | First Name Match |
|
Newest |
The target field has the most recent date among all records queried |
|
Oldest |
The target field has the most distant date among all records queried |
Newest and Oldest are most useful for duplicate matching on child records, because in that case they will only be applied to those child records that are under an already matched parent record.
Duplicate Matching Rules also offers a number of other relative date functions, only available if the target field is a Date or Date/Time field. These functions are identical to the functions that are standard in Salesforce view and report filtering. Details are listed here https://help.salesforce.com/apex/HTViewHelpDoc?id=custom_dates.htm
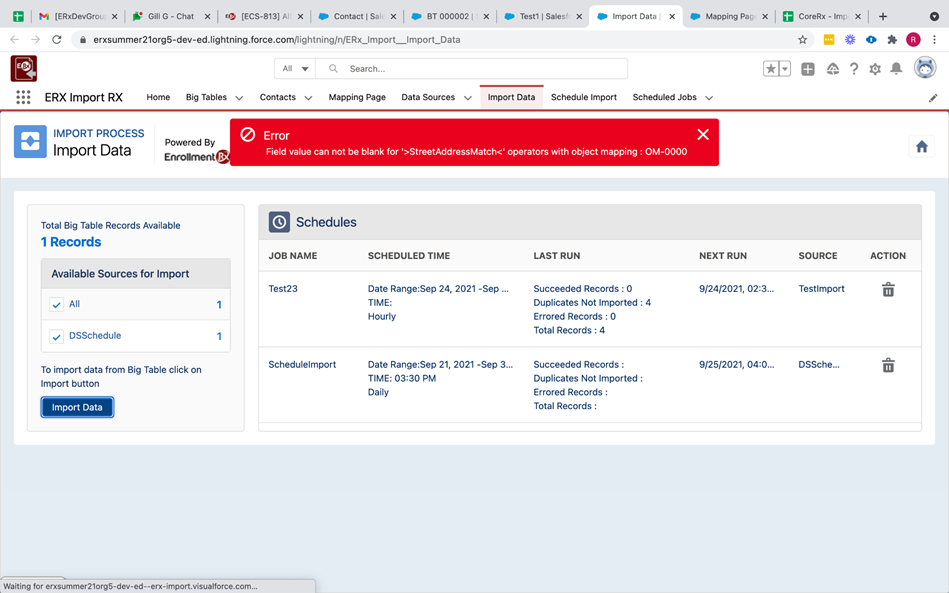
Operators that Do Not Support Null Values
Whenever the below mentioned operators are being used in any condition for any fields in Duplicate Matching Rules on the mapping page, those fields value cannot not be null (empty) while importing data.
- Contains
- Includes
- Excludes
- Does Not Contain
- Starts With
- Less Than
- Greater Than
- Less or Equal
- Greater or Equal
- First N Characters
- Street Address Match